An All-inclusive Guide: What Are The Computer Devices?
Introduction
In this digital era, computers are an integral part of our daily lives. They have revolutionized the way we work, learn, and communicate. But what exactly are computer devices, and how do they work? This comprehensive guide aims to simplify and provide a deep understanding of the different types of computer devices, their roles, and functions. Let's delve deeper into this fascinating world of computers.
What are Computer Devices?
Computer devices, often termed as computer hardware, are the physical components that team up with software to complete numerous tasks. Think of computer devices as the building blocks that, when working harmoniously, pave the way for seamless computer operation. Their role is quintessential – from letting you enter data to processing it and presenting the final output. For better comprehension, we can classify these devices into five crucial categories. Let’s take a quick tour of these categories:
1. Primary Computer Devices: The backbone of computers that includes key elements like the Central Processing Unit (CPU) and the motherboard.
2. Memory and Storage Devices: These are vital devices that aid in storing both temporary and permanent data. This involves Random Access Memory (RAM), Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), Solid State Drives (SSDs), and more.
3. Input and Output Devices: The mediums through which we interact with computers. This includes devices like keyboards and mice (input devices) and monitors and printers (output devices).
4. Networking Devices: These devices enable interconnection between multiple computers, such as routers, modems, and switches.
5. Peripheral Devices: Additional hardware that enhances the functionality of computers. Examples include printers, scanners, webcams, game controllers, etc.
That's a broad picture of computer devices and their categorization. Let's delve deeper into each category and understand how they matter in the functioning of a computer!
What Makes up the Primary Devices of The Computer?
Decoding the Central Processing Unit
- Origin: Often referred to as the computer's "brain," the Central Processing Unit (CPU) is a primary device that performs most of the processing inside computers.
- Function: This vital component carries out instructions of a computer program by performing the basic arithmetic, logical, control and input/output (I/O) operations.
- Composition: The CPU houses two important sub-devices – a Control Unit (decodes instructions from the memory and transforms them into signals) and Arithmetic Logic Unit (handles arithmetic and logical operations).
- Significance: As the CPU processes most of the data, its speed (and therefore performance) significantly affects the computer.
The Motherboard's Key Role in Computers
- Alias: Known as the "spinal cord" of the computer, the motherboard is another primary device.
- Function: As a central communication backbone, it facilitates communication between all the components of the computer, ensuring they work in harmony.
- Composition: The motherboard hosts critical parts including the CPU, memory (RAM), hard drive, graphics card, sound card, and interfaces for peripheral devices.
- Significance: Your computer's capabilities and future upgrading opportunities largely depend on the selection of a suitable motherboard. It determines the type and amount of RAM, the support for CPUs, and other expansion cards.
In conclusion, the CPU and the motherboard are the primary and most essential devices found within a computer. They work hand in hand to ensure your computer performs at its best, providing a basis for all other computer interactions. Their effectiveness and efficiency ultimately dictate the overall performance capabilities of your computer system.
What Are The Essential Storage and Memory Devices?
Distinction between Memory and Storage Devices
Memory or RAM and storage devices are vital components of a computer with diverse roles.
- Memory or RAM: Known as Random Access Memory, serves as a temporary data holder for the CPU. The critical point is, it's volatile by nature – any unsaved data will vanish once the computer is off.
- Storage Devices: Unlike RAM, storage devices preserve data for the long-term and of course, they are non-volatile. Examples include hard drives, SSDs, flash drives, and more.
Understanding the functions of these devices is crucial in determining a computer's processing speed and storage capacity.
Unmasking the World of HDDs, SSDs, and Beyond
In the landscape of storage devices, HDDs, and SSDs are the prime players, accompanied by other devices like CDs, DVDs, and USB flash drives. Here's a simple breakdown:
1. Hard Disk Drives (HDDs): Traditional yet effective, HDDs record data on rotating magnetic platters. The speed depends on the rotation speed of the disk (measured in RPM - Revolutions Per Minute).
2. Solid State Drives (SSDs): A modern alternative to HDDs, SSDs are way faster and use flash-based memory. As there are no moving parts, they tend to be more durable and efficient.
3. USB Flash Drives & Optical Discs: Portable USB drives store data on flash memory, while CDs and DVDs use lasers to read/write data.
When purchasing storage devices, consider factors like storage space, price, speed, and durability. Understanding these components guides you to make a more informed tech decision, tailoring your computer to your specific needs.

How Do Input and Output Devices Relate to Computers?
Input and output devices act as the communication bridge between the user and the computer, directly impacting the interaction between the two.
A Horizon Beyond Keyboards: A Tour Through Diverse Input Devices
Input devices are essentially mediums for the user to relay instructions or data to the computer. While keyboards and mice are the most known, let's broaden our perspective:
- Microphones: These transform the user's voice into an electrical signal which is then converted into digital data recognizable by the computer. Useful for voice recognition software and vocal commands.
- Cameras: Used for capturing images or videos, they change visual information into a digital format which the computer can process. Crucial for video calls, virtual meetings, and more.
- Scanners: These devices serve to digitize physical documents, converting images into a form that the computer can read and store.
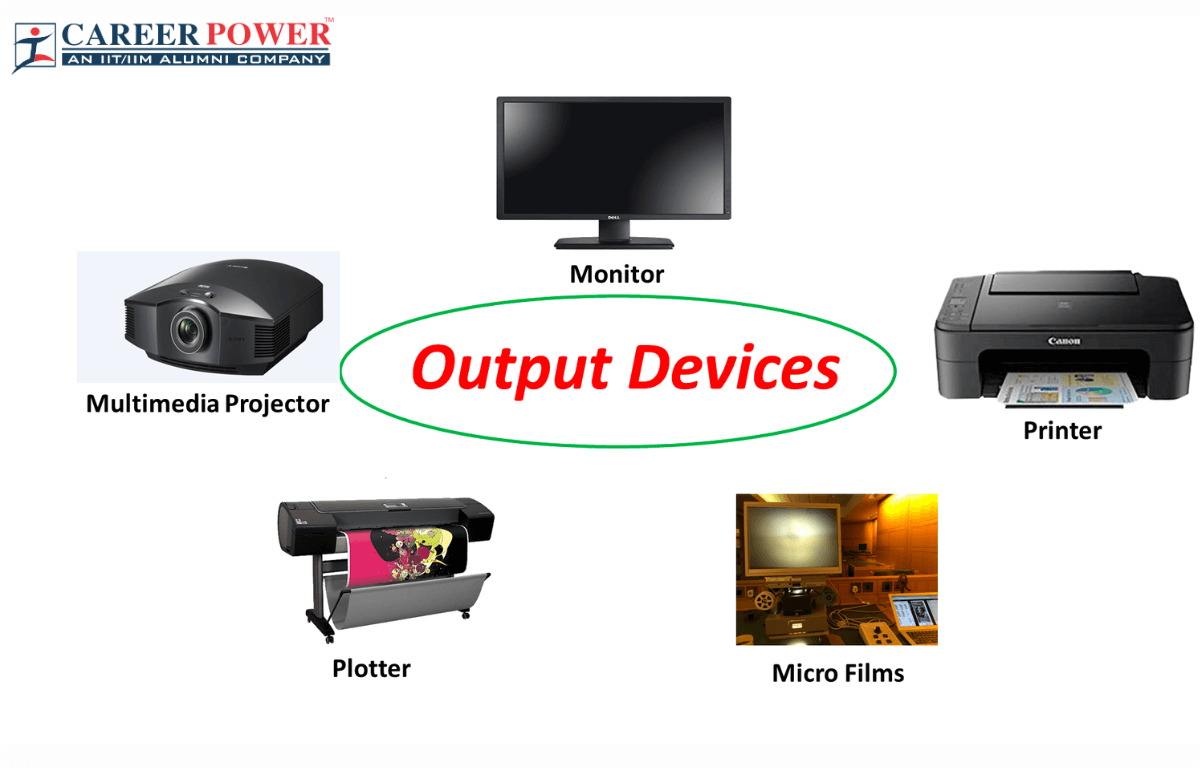
Beyond Display Screens and Printers: Diving Into the Universe of Output Devices
Output devices translate the computer's processed data into a comprehensible format for the user. Though monitors and printers are quite well-known, there are more to explore:
- Monitors: They convert the digital signals from the computer into images or texts that are displayed to the user.
- Printers: These devices generate hard-copy outputs of the processed data, be it pictures or documents.
- Speakers: Pivotal for audio output, they convert digital signals into sound waves, enabling the user to listen to music, voice, and other sounds.
- Projectors: Similar to monitors, they enlarge the visual output onto a larger screen, ideal for presentations.
Understanding the diversity and significance of input and output devices unravels the reality of how interactive and versatile computers can be.
What are Networking and Peripheral Devices in Computers?
These devices pave the way for enhanced connectivity and extended functionality diverse computer operations.
The Backbone of Connectivity - Networking Devices
Networking devices are integral components that ensure efficient data flow between computers in a network setup - an enabler for effective communication. Primarily, they are categorized into:
- Modems: These data transmission devices convert digital data into analog signals and vice versa. Crucial for broadband connections, they establish a bridge for Internet connectivity.
- Routers: A cornerstone in setting up a home or office network, routers direct data along its network path, ensuring seamless WiFi connectivity.
- Switches: Often underestimated, switches act as the controller guiding the data flow between devices in a network. They channel network data to the correct device smoothly, reducing the risk of data collision.
Enhancing User Experience with Peripheral Devices
Peripheral devices, while not essential to the basic functionality of the computer, significantly enrich the user interface and system capabilities. These include:
- Printing Devices: Printers and scanners, facilitating the transition from digital data to physical medium and vice versa, are indispensable in today's digital age.
- Game Controllers: Adding a layer of interactive immersion, these devices enhance the gaming experience for users.
- External Storage Devices: Devices like external HDDs and SSDs offer extended storage options, accommodated files that exceed the internal storage capacity.
In sum, networking and peripheral devices play pivotal roles, contributing ineffably to the smart, efficient, and versatile functionality that computers offer today.
Conclusion
In summary, computer devices play a crucial role in how we interact and use computers. From primary devices like the CPU and motherboard, storage and memory devices, input and output devices to networking and peripheral devices, each has particular roles that ultimately allow computers to function as cohesive, effective units.
Related FAQs about what are the computer devices
How does a Central Processing Unit work in a computer?
The Central Processing Unit (CPU), also known as the computer's brain, executes instructions from a computer's software. It fetches the data or instructions from memory, decodes the fetched data, sends it for processing or computation, and finally stores it accordingly. It does this using two internal components – the Control Unit and the Arithmetic Logic Unit.
What is the difference between memory and storage devices in computers?
Memory, also known as RAM, is temporary storage that stores the data the computer is currently processing. It's volatile, meaning it doesn't retain information when the power is turned off. On the other hand, storage devices like HDDs or SSDs store data permanently. Information stored in these devices remains intact even when the device is powered off.
What are some examples of peripheral devices and their uses?
Peripheral devices are external hardware that provides additional capabilities to the computer. Examples are printers (produce hard copy outputs), scanners (convert physical documents into digital format), speakers (produce audio output), and game controllers (enhance game interaction). Thus they enhance the functionality and user interface of computer systems.