Uncovering 3D Printing: What Materials Do 3D Printers Print With?
Introduction
Dive into the fascinating world of 3D printing where the digital becomes tangible. Here, we explore the expansive range of materials used in 3D printing, how they influence the properties of the end product, and how technology advancements are broadening these capabilities. Whether you're a hobbyist, a professional, or just curious, this comprehensive guide will illuminate the what, why, and how of 3D printing materials.
What is 3D Printing and How Does It Work?
Imagine a technology that can convert your virtual design into a physical object - welcome to 3D printing! In a nutshell, 3D printing, also often known as additive manufacturing, introduces a ground-breaking approach to transform a simple digital file into a three-dimensional object. Here's how it operates:
- Creation of a Digital Design: This journey begins with designing a 3D model on the computer. This digital blueprint will serve as the guide for the 3D printer.
- Layer Upon Layer: Differing from traditional manufacturing methods, 3D printing employs an additive process. It constructs the object layer by layer, each serving as a thinly sliced, horizontal cross-section of the final product.
- Material Matter: 3D printing isn't restricted to just one type of material. It has a wide bandwidth of materials it can print with, ranging from plastics and metals to revolutionary mediums such as organic materials.
- Fabrication: The digital blueprint is now ready for the 3D printer. The printer then meticulously follows each digital slice, lays down the material accordingly, and voilà, the object gradually takes shape.
To summarize, 3D printing amalgamates digital technology with the physical world, making the possibilities of creation virtually limitless! The process of transforming digital files into three-dimensional products is indeed revolutionizing how we create and produce objects.
What are the Basic 3D Printing Methods and Their Corresponding Materials?
3D printing, a realm of incredible ingenuity, utilizes various methods to transmute abstract concepts into tangible creations. Each method corresponds to different materials, bringing about a distinctive final product. Here, we spotlight the three primary 3D printing methodologies and detail which materials pair best with them for optimal results.
1. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM):
FDM finds its widespread popularity from its affordability and diversity in material choices. It operates by heating and extruding a thermoplastic filament layer by layer until the object is fully formed.
- Primary Materials: The most used materials for FDM include Polylactic Acid (PLA) and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), famed for their versatility, ease of use and bio-degradable nature.
- Unique Material Creations: The filament can also be composed of wood, metal, and various other materials, thus opening up a world of different finishes and properties.
2. Stereolithography (SLA):
SLA is truly a marvel as it utilizes light to craft intricate 3D structures. This process involves curing a liquid plastic resin with an ultraviolet laser, solidifying it layer by layer until the final object takes shape.
- Primary Material: Plastic-based photopolymer resin is typically used due to its advanced properties, such as high resolution and smooth finish.
3. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS):
This method, unlike the previous two, employs powdered materials. A powerful laser selectively sinters, or melts, these powders, turning them into a strong, solid structure.

- Primary Materials: SLS printers primarily use powders like nylon, polyamide, or metals like steel, titanium, and aluminum, due to their high durability.
These categories broadly encapsulate the most basic 3D printing techniques. However, the evolution of technology continually revolutionizes this space with more advanced methods and unique materials, all contributing to the expansive versatility of 3D printing. No matter the material or the process, the essence of 3D printing lies in transforming the digital into the physical, the dream into the real.
What are the Most Common Materials Used in 3D Printing?
Let's delve into the world of 3D printing to uncover the materials most commonly employed for producing three-dimensional prints. Each material comes with its own set of properties, suiting distinct applications and yielding different outcomes. Here's a comprehensive account of the materials that prevail in the 3D printing industry:
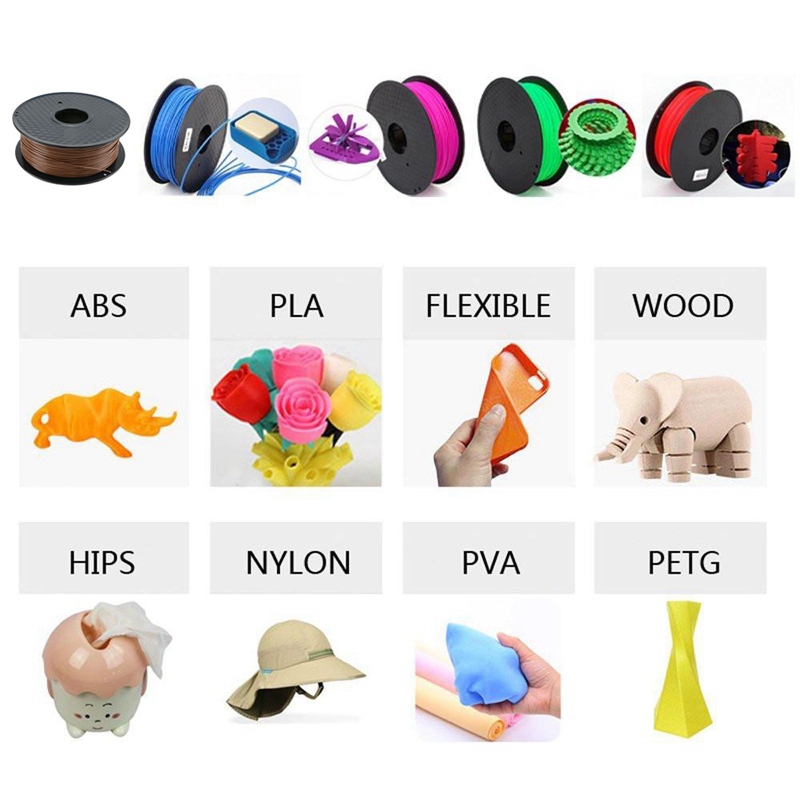
1. Plastics: In the universe of 3D printing, plastics undoubtedly reign supreme, specifically in Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) printing. The two types of plastics that take the lead are:
- Polylactic Acid (PLA): Viewed as the champion of eco-friendly options, PLA is made from fermented plant starch such as corn or sugar cane and is recognized for its simple usability and intriguing glossy finish.
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): A petroleum-based plastic, ABS is appreciated for being resilient, impact-resistant, and capable of withstanding higher temperatures. It's frequently the material of choice for toys, tools, and other durable items, reflecting its robust nature.
2. Resins: Typically employed in Stereolithography (SLA) printing, plastic-based resins promise smooth surface finishes and a high level of detail. These characteristics make resins an ideal choice for prototypes, jewelry, and dental and medical applications.
3. Metals: Metals might not be the first choice for all, but their usage allows for the production of strength-oriented, extremely durable 3D components. The Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) method often employs metal powders, with popular choices including:
- Steel: Known for its strength and durability.
- Titanium: Prized for its high strength-to-weight ratio.
- Aluminum: Loved for its lightness and corrosion resistance.
Choosing the right material for 3D printing is pivotal. It heavily influences not only the aesthetic appeal of the print but also the object's functional capabilities significantly. With an array of materials like plastics, resins, and metals at your disposal, the possibilities are indeed endless.
What are Some Innovative Materials Being Used in 3D Printing?
The dynamic field of 3D printing continuously opens new frontiers, with innovative materials leading the charge. Here are some trailblazing substances revolutionizing additive manufacturing:
1. Bio-materials: These materials are a perfect blend of technology and nature, allowing printing with live cells to construct organic tissues. The biomedical field is ripe with possibilities, from cultivating skin grafts to heart valves, disrupting the way healthcare is delivered.
2. Graphene: Riveting attention for its extraordinary strength and conductivity, graphene breathes new life into high-strength additive manufacturing. It opens up avenues for printing top-notch electronic equipment and devices.
3. Wood Filament: This mixture of PLA with small wood fibers gives 3D printed objects a charming look and feel reminiscent of authentic wood. It's a great choice for decorative items, jewelry, and even architectural models.
4. Ceramics: This high-quality material offers heat resistance alongside a glossy finish. Ceramics have a vast range of applications, from making kitchenware and home decor to crafting dental prosthetics and heat-resistant components.
These innovations in 3D printing materials inspire designers, engineers, and hobbyists to push the bounds of creativity and functionality, transforming what's possible with 3D printing technology.
How Do Material Choices Affect the Properties of 3D Printed Objects?
The selection of materials considerably shapes the end qualities of 3D printed items. Below is a list outlining the impacts various material choices have on 3D printed objects:
- PLA (Polylactic Acid): This material creates 3D prints with a glossy, smooth surface, making it popular for aesthetic objects. However, its brittleness means it's not appropriate for elements required to withstand robust use.
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): Chosen for its strength and durability, ABS produces prints that, while slightly rougher in texture compared to PLA, are known for their hardcore functionality, ideal for making mechanical components.
- Resin: Resin is a top choice for items requiring small-scale detailing and smooth finishes. Miniature models and figurines are often produced using resin due to these characteristics.
- Metals: In 3D printing, metallic materials, such as steel, titanium, and aluminium, offer unparalleled toughness and durability among material selections. This makes them ideal for creating industrial-grade parts.
Exploring uncharted material choices like bio-materials or ceramics, we witness a whole new world of possibilities in the realm of 3D printed creations.
In summary, the material you select significantly influences your 3D print's appearance, feel, durability, and functionality. Therefore, the material choice would always depend on the requirements of the final product.
Conclusion
3D printing is a versatile technology with an ever-expanding variety of materials. This means that the scope of what can be created is only limited by our imagination. Whether it's intricate miniatures, rugged mechanical parts, biological tissues, or dazzling ceramic art pieces - 3D printing materials offer something for everyone.
Related FAQs about what materials do 3d printers print with
What is the difference between FDM and SLS printing?
FDM and SLS are distinctive 3D printing methods. FDM, or Fused Deposition Modeling, heats and extrudes a plastic filament layer by layer to form the object. On the other hand, SLS, or Selective Laser Sintering, uses a laser that sinters powdered material layer by layer, forming a solid structure. They use different materials, with FDM commonly utilizing PLA or ABS filaments, while SLS mainly employs powdered substances such as nylon.
Can 3D printers use sustainable or recycled materials?
Yes, 3D printers can work with sustainable and recycled materials. PLA, one of the most popular materials for 3D printing, is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources like cornstarch or sugar cane. Additionally, recycled plastics can be used to make filaments for FDM printers, contributing to waste reduction and promoting sustainability.
How are advances in technology broadening the capabilities of 3D printer materials?
Technology advances continually enhance the capabilities of 3D printer materials. We're witnessing development in terms of material strength, flexibility, and variety. Innovations are leading to materials like bio-materials and graphene entering the scene, which can craft live organic tissues and high-strength electronic equipment, hence opening up entirely new fields of applications for 3D printing.