Unlocking the Mystery of Wdr in Cameras: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In the realm of photography, WDR or Wide Dynamic Range is a crucial concept that can significantly impact the quality of your images. However, understanding what WDR is and how to properly utilize it can often seem like a daunting task. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of WDR, its function, its importance in high-quality photography, and its benefits, as well as its limitations. We will also provide practical tips on how you can reap the benefits of WDR in your photography practice.
What is WDR in Camera Technology?
Wide Dynamic Range, adequately abbreviated as WDR, is a technologically advanced feature that exists within the expansive world of digital cameras. This exceptional technology excels at producing superior quality photos in environments where the lighting conditions fluctuate considerably.
• Wide Dynamic Range or commonly known WDR basically handles significant light intensity variations that exist within a single scene.
• WDR allows cameras to produce pictures high in detail, capturing more clarity in both the darkened areas (shadows) and intensely lit spaces (highlights) alike.
• One might ask, 'how does WDR achieve this distinct quality?' It's quite intriguing. WDR functions by fusing multiple images (each having distinct exposure levels) together to form a perfectly balanced final image.
• In essence, when you capture an image with a WDR feature, your camera actually takes multiple shots at differing exposure levels.
Here is how it operates:
1. The camera captures an underexposed image to maintain details in well-lit areas.
2. An accurately exposed photo for the neutral areas is taken.
3. A third overexposed image is taken to maintain the necessary details in the darker regions.
Finally, the camera merges these multiple exposures into one image, resulting in an enhanced final image with incredible highlight and shadow detail representation. So, not only does the WDR function efficiently in high-contrast environments, but it also expertly takes care of the lighting balance within a scene.
How does WDR Function in a Camera?
In comprehending how WDR functions in a camera, the process can be broken down into discrete steps, which help highlight its power and effectiveness. The following description explains the functioning of WDR in a simplified manner:
1. Multiple Snapshots: When shooting a high-contrast scene, the camera's WDR technology takes multiple consecutive shots at varying exposure levels. This includes an underexposed shot focusing on well-lit spots, a correctly exposed image for normally lit areas, and an overexposed image for darker regions.
2. Image Contrast: The underexposed shot aims to prevent loss of detail in brighter regions by limiting the light exposure. Inversely, the overexposed image ensures that details are captured in less lit parts of the scene. The optimally exposed shot takes care of similarly lit portions of the scene, ensuring a balanced result.
3. Image Fusion: These pictures, each with their respective light exposures, are then combined or fused together. The result is a picture that maximizes detail capture, whether in the shadows or the highlights.
4. Enhanced Detail Capture: The fusion of these differently-exposed images allows the camera to output a final, single image. This combined image effectively retains more detail from both the highlight and shadow areas, offering an accurate and realistic portrayal of the contrast found in real-life scenes.
So, WDR's role is to harmonize the contrasts between light and shade that naturally occur, providing us with photo images that mirror exactly what our eyes see in terms of lighting variations.
Why is WDR Crucial for High-Quality Photography?
The contribution of Wide Dynamic Range (WDR) to high-quality photography is extremely significant. This comes down to several crucial factors detailed below:
1. Balancing Lighting Contrasts: One of the main functions of WDR is the smooth handling of strong lighting contrasts in a single frame. This essential feature helps to create clear and detailed images irrespective of the challenges posed by the lighting situation.
2. Consistency in Color Balance: WDR technology plays a pivotal role in maintaining color balance across an image. It works to ensure the reduction of both overexposure in brightly lit parts and underexposure in darker areas.
3. Representation of Real-Life Scenarios: WDR enhances the camera's ability to capture the depth and richness of scenes accurately. This process results in images that more precisely reflect the variations in contrast and color of the real-time views.
4. Enhancing Detail Orientation: The use of WDR greatly enhances the level of detail the camera can capture. This includes details in both the shadowed and highlighted areas of a photograph subject to contrasting light levels.
By successfully capitalizing on these capabilities of WDR in photography, photographers can create stunning and captivating images that echo reality's depth and richness. The correct amount of light exposure in combination with the right color balance can transform an ordinary photograph into an emotional and memorable moment captured in time.
What are the Benefits and Limitations of using WDR in Cameras?
The application of Wide Dynamic Range (WDR) technology in cameras has proven to be largely beneficial in photography. Yet, it is essential to note that its use is not without limitations. Here, we provide a comprehensive list outlining the advantages and potential drawbacks of using WDR in your camera.
The Benefits of Using WDR
WDR technology provides a range of substantial advantages that enhance the overall image quality:
- Superior Light Handling: WDR effectively captures images in all lighting conditions, making it excellent for scenes with varied light intensities.
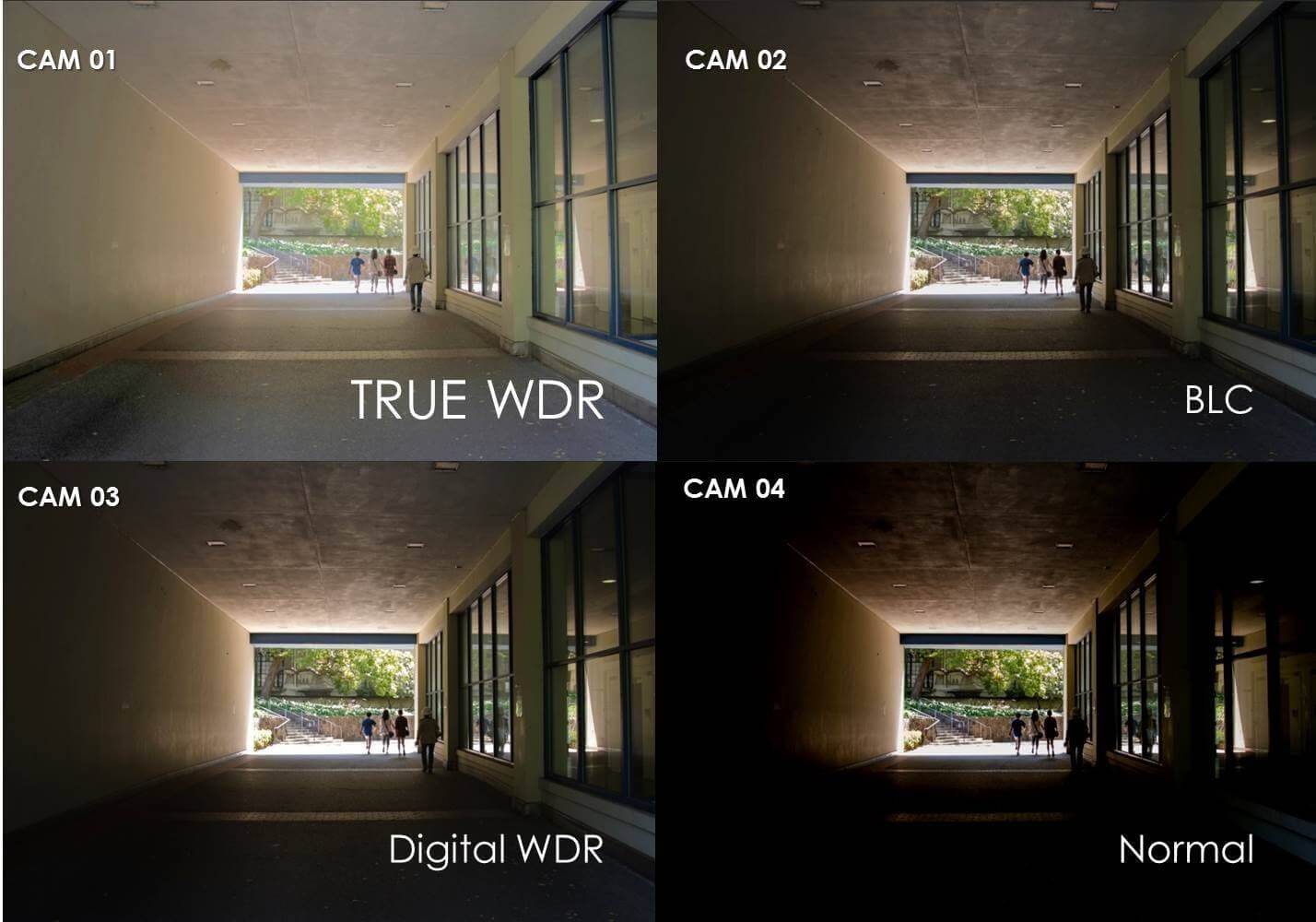

- Enhanced Detail: With WDR, images maintain a high level of detail, even in areas of shadow and highlight.
- Improved Image Quality: The use of WDR often results in overall better quality images, especially in challenging lighting situations.
- Vivid Colors: By balancing the contrast, WDR inevitably enhances the range and vibrancy of colors captured in photographs.
The Limitations of Using WDR
Despite the numerous benefits WDR offers, it is important to be aware of its few limitations:
- Increased Processing Power: WDR often requires more computational power, which may slow down your camera's processing time.
- Less Effective in Extreme Light Conditions: WDR may fail to deliver the desired results in extremely bright or dark environments, leading to potential overexposure or underexposure.
- Additional Time Required: As WDR combines multiple images at different exposure levels, it could take more time to process and create the final image.
In conclusion, while the advantages of using WDR in cameras are numerous and significant, it is equally important to consider its limitations before deciding on its use in your photography practice. Being cognizant of both aspects will empower you to make the best use of WDR technology for your specific needs in photography.
Practical Tips: How can you Best Utilize WDR in Your Photography?
To optimize the use of Wide Dynamic Range (WDR) technology in your photography, it is essential to understand the lighting conditions of your scene and adapt your strategy accordingly. Here are some points to keep in mind:
1. Assess the Lighting Conditions: WDR technology thrives in mixed lighting conditions. So, if you're photographing a scene with a combination of bright and dimly lit areas, WDR can help balance out those extremes and produce a more evenly exposed image.
2. Configure the WDR Settings: Depending on the scenery and lighting situation, adjust the WDR settings on your camera accordingly. Most cameras allow you to dial-in the degree of WDR you want to apply, enabling you to control how much shadow and highlight detail is rendered in your photos.
3. Avoid Extreme Lighting Situations: WDR is great for balancing out light and dark areas, but it might not give the best results in environments that are too bright or too dark. In very bright conditions, the shadows might appear too dim relative to the highlights, and in extremely dark conditions, the photo may appear grainy or noisy.
4. Use Alongside Other Lighting Techniques: It is important to remember that while WDR can enhance your images significantly, it shouldn't replace good lighting techniques and equipment. Use it as an adjunct to your other photographic skills and resources, and not as a crutch.
By understanding when and how to use WDR effectively, you can take your photography to the next level, capturing images that are more dynamic, vibrant and realistic.
Conclusion
Understanding WDR in camera technology can greatly enhance the quality of your photographs. By properly utilizing this feature, you can capture more detailed and well-balanced images, even in challenging lighting conditions. The potential limitations are minuscule when compared to the advantages WDR can provide. Incorporate WDR into your photography practice, and witness the remarkable difference it can make.
Related FAQs about what is wdr on a camera
How is WDR different from HDR in camera technology?
While both WDR and HDR aim to balance high contrast scenes, their methods vary. WDR, or Wide Dynamic Range, combines multiple images at different exposure levels captured simultaneously. In contrast, HDR, or High Dynamic Range, involves combining images taken at different moments and interpolating the varying pixel values to capture a broad spectrum of light and dark details.
In what scenarios does the usage of WDR stand out in photography?
WDR is notably useful in scenes with a wide variation in lighting. This includes environments with extreme contrasts such as sunset or sunrise settings, indoor areas with outside views, or spaces with harsh artificial lighting mixed with shadow areas. In these situations, WDR can create balanced, detailed imagery.
What potential drawbacks should one expect when using WDR features in a camera?
Some potential limitations of using WDR include increased processing power and time, causing a potential slowdown in your camera's functionality. Also, WDR may not be as effective in extremely bright or very dark environments, risking overexposure and underexposure.